Lithium-Ion Vs. Lithium-Polymer Batteries: Whats the Difference?
What Is a Standalone Battery Backup System?
Before we explore the battery world without solar, let's start with the basics: what exactly is a battery backup system?
A battery storage system (or BESS) is a device that stores electrical energy for later use. Typically, address power outages, or peak shaving.
How A Battery Backup Works When without Solar
The key difference between a solar battery system and a battery backup without solar is the charging source of the battery.
Instead of relying on sunlight and solar panels to charge the batteries, a standalone system would draw power directly from the electric grid. In some cases, it can also be charged by other non-solar sources, such as a gas or diesel generator, making it versatile for areas with frequent grid outages.
This means you don't need to invest in solar panels, inverters, or mounting equipment. A system with no solar energy simply charges when grid power is available and kicks in automatically when the grid fails.
Core Components of a Standalone Battery Backup System
A home battery backup without solar panel system relies on four key components.
Battery: Most backup systems use lithium batteries (e.g., LiFePO4) because of their smaller size, long-lasting, and high energy density.
Inverter: Converts the DC power from batteries into AC power to be used by most household and commercial appliances.
Charger: Smart chargers can adjust charging speeds based on grid demand and battery health.
Transfer Switch: When there is an outage, they can automatically switch from grid power to battery power. It can also prevent energy backfeeding, which can be dangerous for workers.
Lithium-Ion vs Lithium-Polymer Batteries: A Comprehensive Comparison
You're looking at a new solar home battery, a laptop, or even just replacing your iPhone battery, and you're faced with a choice: Lithium-ion or Lithium-polymer? These two terms are everywhere, but what do they actually mean for you? Is one fundamentally better, or are they just suited for different jobs?
Understanding the difference between lithium ion and lithium polymer battery is key to choosing the right technology for your needs, whether it's for maximum safety in your home or a slim design in your phone. Let's break down these two powerhouses.
What Are Lithium-Ion Batteries?
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are the workhorses of the modern portable power world. They use a liquid chemical electrolyte to facilitate the flow of lithium ions between the anode and cathode. Think of them as a reliable, high-capacity water bottle—efficient and proven.
You'll find them in:
Electric vehicles
Power tools
Laptops and many smartphones
Home energy storage systems (like many 10kwh home battery units)
What Are Lithium-Polymer Batteries?
Lithium-polymer (Li-Po or Li-Poly) batteries are a more modern variant. Instead of a liquid electrolyte, they use a solid or gel-like polymer electrolyte. This key difference between li-po and li-ion allows for much greater flexibility in shape and size.
You'll typically find lithium polymer battery tech in:
Ultra-thin laptops, smartphones, and tablets
Radio-controlled drones and hobby equipment (often as lipo batteries)
Wearable devices
What are the Differences Between Lithium-Ion Batteries and Lithium Polymer Batteries?
While both are rechargeable and based on lithium, the battery li ion vs li polymer debate comes down to several key characteristics.
Composition: Liquid vs. Polymer
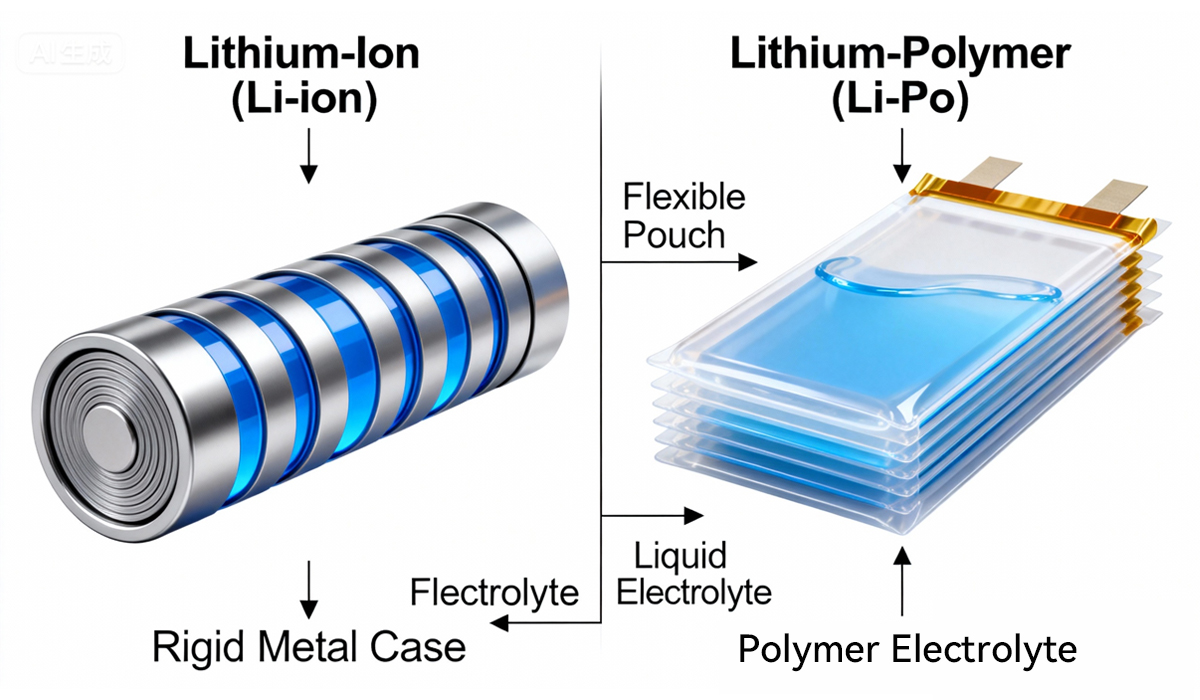
This is the fundamental difference between li ion and li po.
Li-ion: Uses a liquid electrolyte, which is highly conductive but requires a rigid, cylindrical or prismatic metal casing.
Li-Po: Uses a solid or gel polymer electrolyte. This allows the battery to be housed in a flexible, lightweight pouch, making it incredibly slim and versatile.
Performance: Energy Density and Lifespan
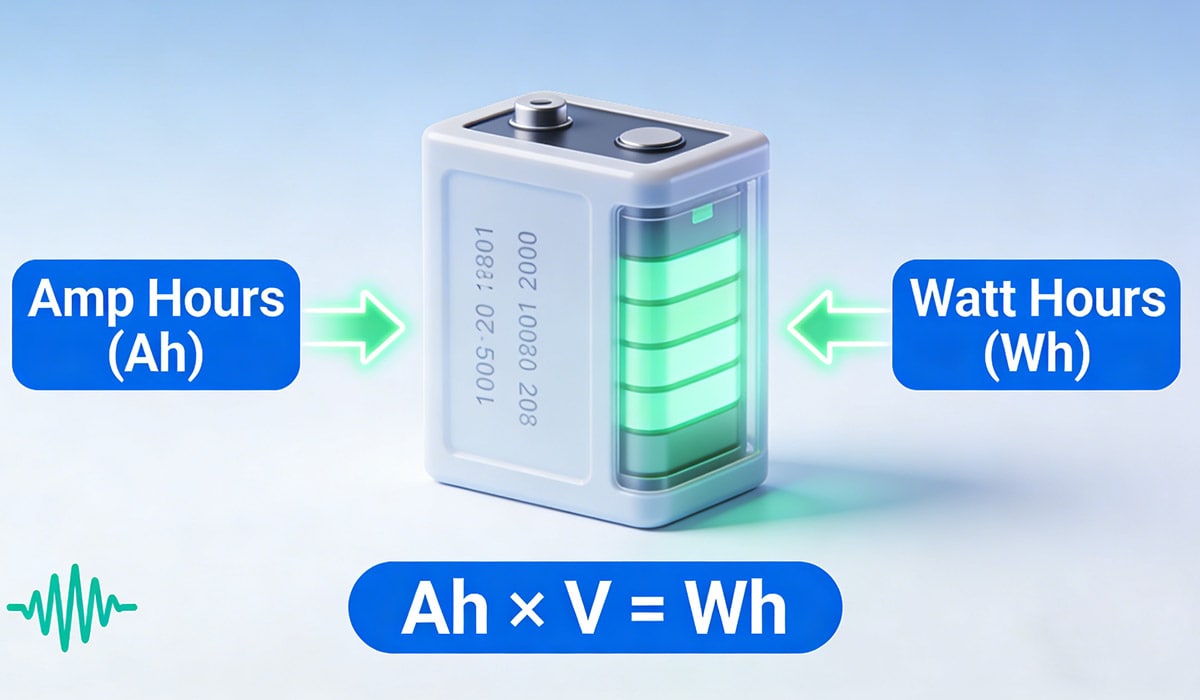
Energy Density: Historically, Li-ion had a higher energy density, meaning it could store more power for its weight. However, advances in lithium polymer battery tech have closed this gap significantly.
Lifespan: Li-ion batteries generally have a longer cycle life (more charge-discharge cycles) before significant degradation occurs compared to standard li polymer battery versions.
Safety and Durability: A Critical Consideration
Safety: This is a major point in the li ion vs lipo discussion. Li-ion batteries with liquid electrolytes are more prone to leaking and can be a fire hazard if damaged or improperly charged. Li-Po batteries are generally more stable and less prone to leakage. However, if a lipo battery is punctured or swollen, it can also pose a significant fire risk.
Durability: The rigid casing of Li-ion offers some physical protection. The pouch of a Li-Po is more susceptible to piercing but is better at resisting swelling over time.
The Costs: Which is More Affordable?
Li-ion batteries are cheaper to manufacture at scale. This is why they dominate in cost-sensitive applications like power banks and home energy storage.
Li-Po batteries are typically more expensive due to the more complex manufacturing process, contributing to the higher cost of the ultra-thin devices they power.
Charging Requirements
Both battery types require careful charging with specific chargers to prevent damage. The question of li-polymer battery how to charge is crucial—always use a charger designed for the specific battery type to avoid overcharging, which can lead to failure or fire in both lipo vs lithium ion.
Battery Applications: Where You'll Find Each One
| Application | Typical Battery Type | Why? |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Vehicles & Home Storage | Lithium-Ion | Best balance of energy density, lifespan, and cost for high-capacity needs. |
| Smartphones & Ultra-thin Laptops | Lithium-Polymer | Flexible form factor allows for slimmer device designs. |
| Power Tools & Drones | Both (Context Dependent) | Li-ion for power and runtime; Li-Po (especially lipo batt) for high burst discharge rates in performance hobbies. |
| Wearables & Small Gadgets | Lithium-Polymer | Ability to be made in custom, small, and thin shapes. |
Lithium-Ion vs. Lithium-Polymer, which is Better?
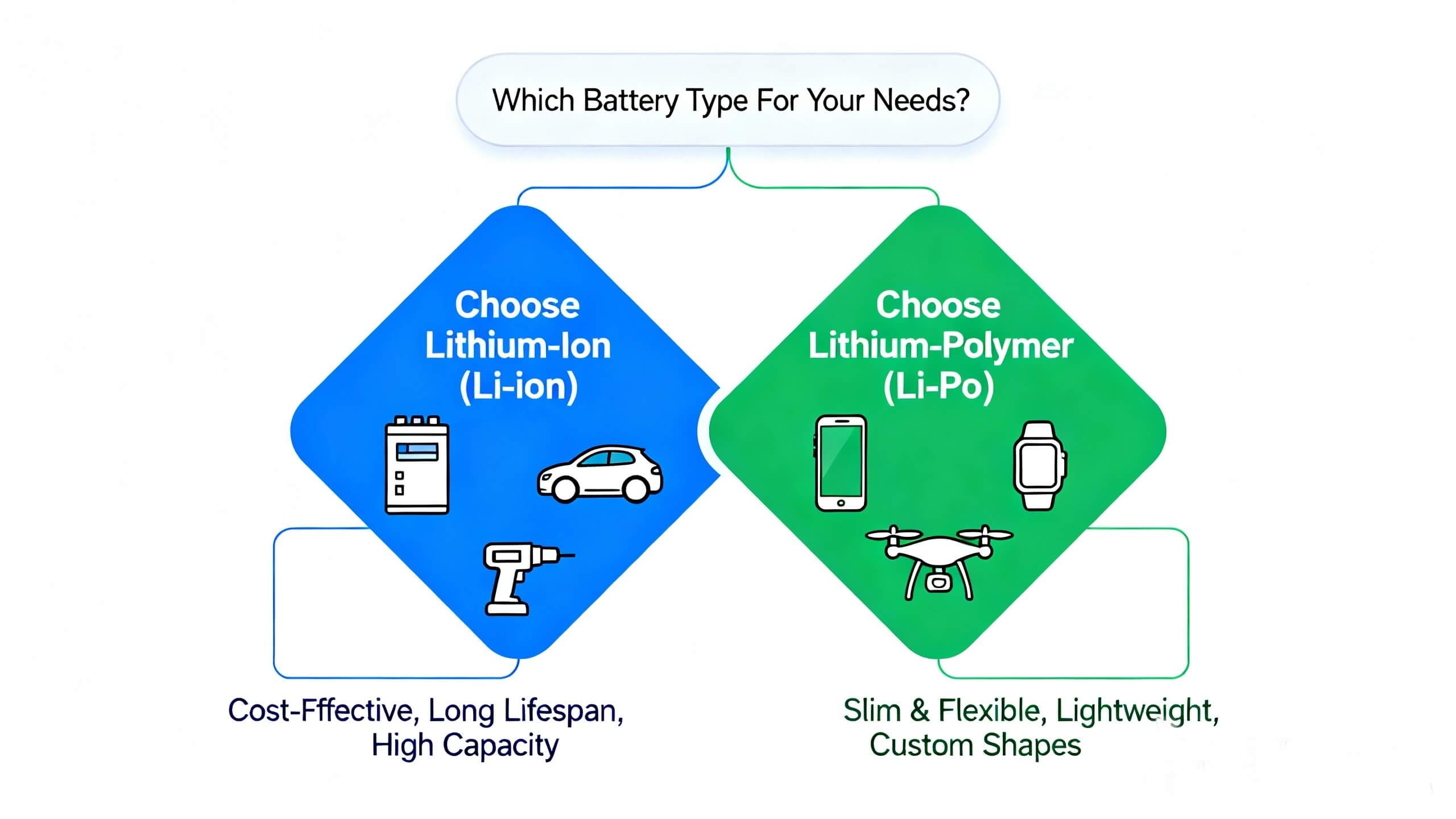
The answer isn't about "better," but about "better for what."
Choose Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) if: You need a cost-effective solution with a long lifespan for high-capacity applications. This makes it the go-to choice for home solar battery storage (like a 10kw battery), electric vehicles, and power tools where size and weight are less critical than reliability and cost per cycle.
Choose Lithium-Polymer (Li-Po) if: Your priority is a lightweight, slim, and flexible form factor. It's ideal for modern smartphones, tablets, and drones where fitting into a tight space is more important than having the absolute lowest cost.
For most homeowners considering a battery 10kw wall unit for solar energy storage, Lithium-ion technology (including its sub-types like LiFePO4) is typically the recommended choice due to its proven track record, longer lifespan, and better cost-effectiveness for stationary storage.
Conclusion
In the lithium ion vs lithium polymer debate, both technologies are exceptional but serve different masters. Li-ion reigns supreme in cost-effective, high-energy applications, while Li-Po provides the design freedom needed for the sleek, portable electronics we use daily.
When making your choice, especially for a significant investment like a home battery, always prioritize the specifications that matter most: safety certifications, cycle life, and total cost of ownership, rather than just the underlying chemistry.
Lithium-Ion vs. Lithium Polymer Batteries FAQs
Q1: What is the main difference between lithium ion and lithium polymer?
The core difference between lithium ion and lithium polymer is the electrolyte: Li-ion uses a liquid, while Li-Po uses a solid or gel polymer, allowing for a flexible, lightweight pouch.
Q2: Which is safer, Li-ion or Li-Po?
Generally, Li-Po batteries are considered more stable and less prone to leakage than traditional Li-ion. However, both can be hazardous if punctured, overcharged, or damaged. Proper manufacturing and a Battery Management System (BMS) are critical for safety in both types.
Q3: Can I replace a Li-ion battery with a Li-Po battery?
Not without careful consideration. While sometimes possible (e.g., in some hobbyist applications), they have different charging requirements and physical form factors. Always consult the device manufacturer or a professional, as a direct swap could be unsafe.
Q4: What does a lithium polymer battery vs ion mean for my phone?
Most modern smartphones, including iPhones, use lithium polymer batteries. This allows manufacturers to create the very thin, light, and compact devices we have today, making efficient use of every millimeter of internal space.
Q5: Are lipo batteries the same as Li-Po?
Yes, LiPo is just a common abbreviation for Lithium-Polymer batteries, especially in the hobbyist sector (e.g., lipo 12v battery for RC cars).

How Can We Help?
Contact