Is a 10kW Battery Enough to Run a House?
Understanding Battery Capacity: What Does 10kW Really Mean?
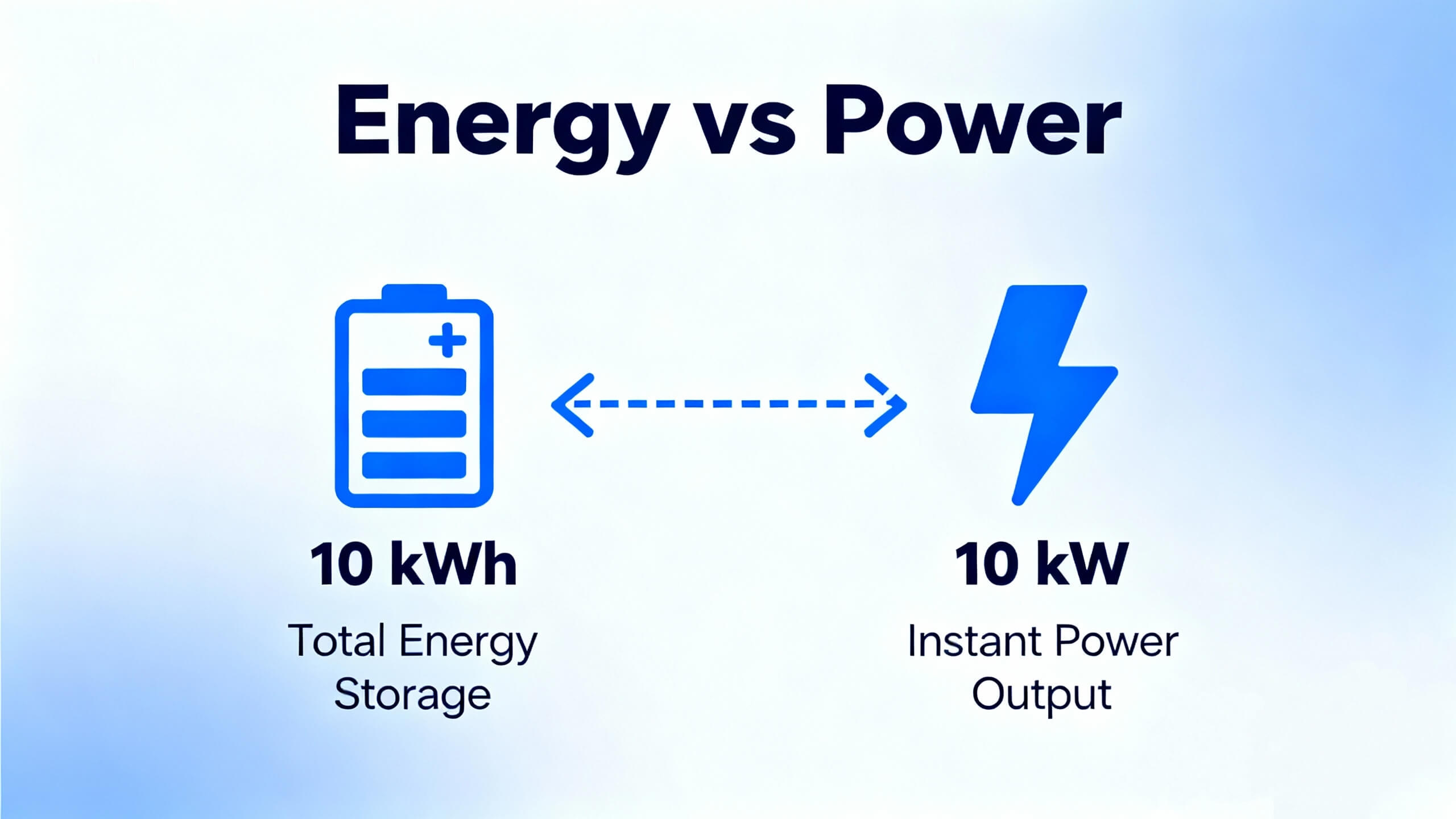
When we talk about a 10kw battery, it's important to distinguish between power and energy. 10 kilowatt hour (10 kwh) refers to the total energy storage—how much electricity the battery can hold. Think of it like a fuel tank: a 10 kwh battery can deliver 10 kilowatts of power for one hour, or 1 kilowatt for 10 hours. Meanwhile, a 10 kilowatt inverter determines how much power you can use at once—for example, running multiple appliances simultaneously.
Key points to remember:
Energy (kWh): The total "fuel" stored in the battery.
Power (kW): The rate at which energy is delivered, controlled by the inverter.
This distinction is vital because a home's energy needs depend on both how much energy you use over time and the peak power required at any moment.
Calculate Daily Energy Consumption: How Much Power Does Your Home Use?
To determine if a 10 kwh battery is sufficient, start by calculating your household's daily energy consumption. On average, a typical U.S. home uses about 30 kWh per day, but this varies based on factors like family size, appliance efficiency, and climate.
Steps to estimate your usage:
Check your utility bill: Look for monthly kWh usage and divide by 30 for a daily average.
List major appliances: Note their wattage and hours of use. For instance:
Refrigerator: 150W running for 24 hours ≈ 3.6 kWh
LED lights: 10W each for 5 hours ≈ 0.05 kWh per light
HVAC system: 3,500W for 2 hours ≈ 7 kWh
Use online calculators or smart meters for accuracy.
If your daily consumption is around 10-15 kWh, a 10kw battery might cover basics, but higher usage requires more storage or solar support.
Estimate Peak Power Demand: Can Your Inverter Handle It?
Peak power demand is the maximum power your home draws at one time—like when the air conditioner, washing machine, and microwave all start at once. A 10 kw inverter can handle up to 10,000 watts, but typical homes have peaks ranging from 5 kW to 20 kW.
Common appliance power demands:
Air conditioner: 1,500–5,000W
Electric stove: 3,000–8,000W
Sump pump: 800–1,500W
If your peak demand exceeds 10 kW, you might experience overloads. Consider a larger inverter or prioritize essential circuits.
Consider Backup Power Needs: What Matters Most During an Outage?
Backup needs depend on your priorities: do you want to power the entire house or just critical loads? A 10 kwh battery paired with a 10 kw inverter can support essentials for several hours, but longer outages require careful planning.
Essential vs. non-essential loads:
Critical: Refrigeration, lighting, medical devices—often totaling 2–5 kW.
Optional: Electric vehicle chargers, pool pumps—these can drain the battery quickly.
For extended backup, integrating solar panels is key. For example, a 13kw solar system can recharge the battery during the day, reducing reliance on the grid.
Assessing Household Energy Needs: Factors That Influence Battery Sufficiency
Every home is unique. To assess if a 10kw h battery fits, consider:
Home size: Larger homes generally use more energy.
Lifestyle: Families with high appliance usage need more storage.
Climate: Heating and cooling can dominate energy bills.
Solar integration: Solar panel performance and average solar panel output per day affect how much energy you generate.
For instance, if you have a solar panels for 10kw system, the solar panel kwh production might offset daily use, making a 10kwh battery more effective.
Can a 10kW Battery Power a House? The Realistic Answer
In short, a 10kW battery can power a house for limited scenarios, but it's not a one-size-fits-all solution. For a energy-efficient home with low daily consumption (under 10 kWh), it might run essentials for a full day. However, for average or high-use homes, it's best for partial backup or paired with solar.
Pros of a 10kw battery:
Compact size, often as a battery 10kw wall unit.
Good for peak shaving and short outages.
Works well with solar to store excess energy.
Limitations:
May not cover high-demand appliances for long.
Requires careful management of energy use.
Example Calculation: Putting It All Together
Let's say a family uses 20 kWh daily. With a 10 kwh battery, they could power critical loads (e.g., fridge, lights, Wi-Fi) totaling 3 kW for about 3–4 hours. But to extend this, they add a 13kw solar system with an average solar panel output per day of 40–50 kWh (depending on location and solar panel performance). This setup recharges the battery, providing longer backup.
Sample energy budget:
Critical loads: 4 kWh per day
Battery capacity: 10 kWh
Solar recharge: 15 kWh from panels
Net result: The battery sustains essentials with solar support, making it viable.
Considerations for Longer Use: Enhancing Your System
For extended power, think beyond the battery. Solar power is needed to run a house efficiently, so evaluate:
Solar panel size and output: The size of solar pv panels and power output of solar panels impact energy generation. Average size of solar panels is around 65x39 inches, producing 300–400W each.
Battery chemistry: Compare options for longevity and efficiency.
Table: Comparison of Battery Chemistries for Home Use
| Chemistry Type | Lifespan (Cycles) | Efficiency | Cost Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium-ion | 3,000–6,000 | 90–95% | $$–$$$ |
| Lead-acid | 500–1,000 | 80–85% | $–$$ |
| Saltwater | 5,000+ | 85–90% | $$–$$$ |
Tips for optimization:
Monitor solar panel kwh production to align with usage.
Consider solar cells cost and incentives for affordability.
Upgrade to a larger system if needed, like a 13kw solar system price ranging from $20,000 to $30,000 before incentives.
Conclusion: Is a 10kW Battery Right for You?
A 10kw battery can be a solid choice for backup power, especially when combined with solar panels. It's enough for essential needs in smaller homes or short outages, but for whole-house coverage or high energy demands, you may need additional storage or a larger solar array. Start by calculating your daily energy consumption and peak power demand, then explore solar options like a 10kw system to maximize efficiency.
Final advice: Consult with a professional to tailor a system to your home. By understanding your energy profile, you can make an informed decision and enjoy reliable, sustainable power.

How Can We Help?
Contact